Grammar
Future tense: review
1. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct tenses.
1. By 2030 all students (have) __________ their own computers in school.
2. I can't come to your party next Friday as I (work) __________ on that day.
3. I know she's sick, but __________ she (be) __________ back to school tomorrow?
4. You (not pass) __________ your exams if you don't start working harder.
5. Whatever job you (decide) __________ to do in the future, I (support) __________ you.
2. Work in pairs. Read the following predictions about the year 2040 and say whether you think it will happen.
Example:
| A: Email will completely replace regular mail. B: I think it will certainly/probably happen. /It certainly/probably won't happen. |
1. We will all be using flying cars.
2. Most people will live to be a hundred years old.
3. Robots will replace teachers.
4. The world will have one money system.
5. The Internet will replace books.
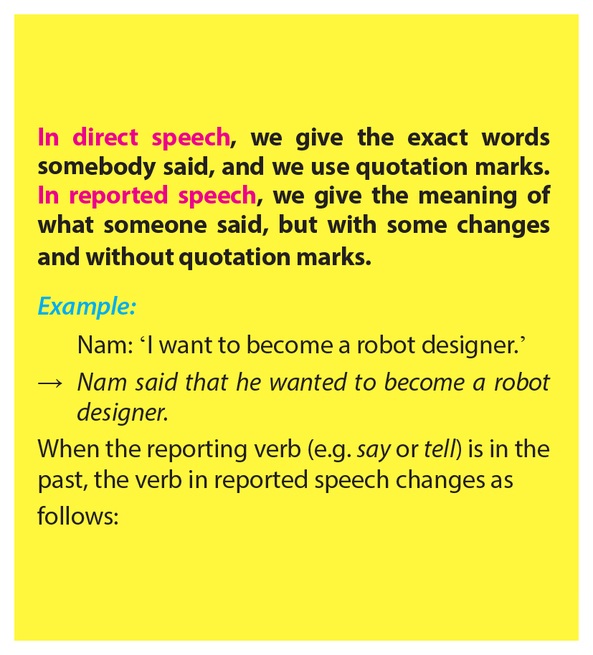
Reported speech
In direct speech, we give the exact words somebody said, and we use quotations marks.
In reported speech, we give the meaning of what someone said, but with some changes and without quotations marks.
Example:
Nam: ‘I want to become a robot designer.’
→ He said that he wanted to become a robot designer.
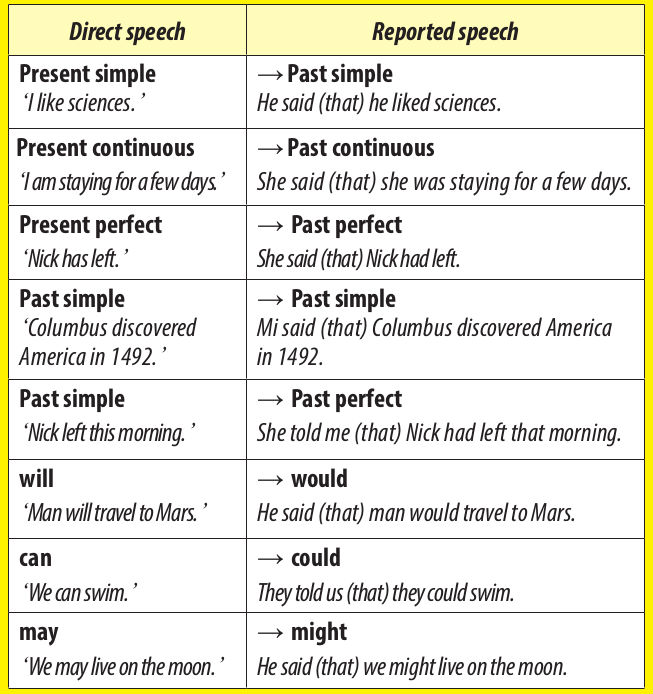
When the reporting verb (e.g say or tell) is in the past, the verb in reported speech changes as follows:
Direct speech Reported speech Present simple
‘I like sciences.’
→ Past simple
He said (that) he liked sciences.
Present continuous
‘I am staying for a few days.’
→ Past continuous
She said (that) she was staying for a few days.
Present perfect
‘Nick has left.’
→ Past perfect
She said (that) Nick had left.
Past simple
‘Columbus discovered America in 1492.’
→ Past simple
Mi said (that) Columbus discovered America in 1492.
Past simple
‘Nick left this morning.’
→ Past perfect
She told me (that) Nick had left that morning.
will
‘Man will travel to Mars.’
→ would
He said (that) man would travel to Mars.
can
‘We can swim.’
→ could
They told us (that) they could swim.
may
‘We may live on the moon.’
→ might
He said (that) we might live on the moon.
Pronouns, and time and place expressions may change in reported speech:
I → he/ she
we → they
you → I/ he/ she
now → then
today → that day
here → there
this week → that day
tomorrow → the following day/ the next day
yesterday → the day before/ the previous day
last month → the month before/ the previous month
Example:
‘I don’t have football today.’
→ He said (that) he didn’t have football that day.

3. Look at the conversation in GETTING STARTED again. Find and underline the examples of reported speech.
4. Complete sentence b in each pair so that it means the same as sentence a, using reported speech.
1. a. Nick: ‘I come from a small town in England.'
b. Nick said that __________.
2. a. My friend: ‘Brazil will win the World Cup.'
b. My friend said that .
3. a. Olive: ‘Chau, I'm leaving Viet Nam tomorrow.'
b. Olive told Chau that __________.
4. a David: ‘Catherine, I'm unable to read your writing.'
b. David told Catherine that __________.
5. a. Minh: ‘I overslept this morning.'
b. Minh said that __________.
5. Change the following sentences into reported speech, using the words given in brackets.
1. ‘I didn't say anything at the meeting last week.' (He said)
2. ‘This letter has been opened.' (She told me)
3. ‘In 50 years' time we will probably be living on Mars.' (Tom said)
4. ‘I hope we will build a city out at sea.' (Mi said)
5. ‘My wish is to become a young inventor.' (Son told us)
6. GAME: MY FRIEND SAID...
Each student stands up or comes to the front of the class. One says a sentence about himself/ herself. The other reports to the class.
Example:
A: I like writing code.
B: She said that she liked writing code.